Other countries, other parasites: Parasite danger when traveling, what to do?
Dogs like to come along on vacation. Unfortunately, the parasites are also waiting, especially in southern countries. Precaution is the order of the day! However, since every country has a different situation, it is not possible to make general recommendations that apply to all countries. However, there are health organizations such as ESCAAP (European Scientific Counsel Companion Animal Parasites), which deal with this intensively.

Please take the ESCCAP travel test online:
http://www.esccap.ch/site/news/der-richtige-parasitenschutz-fur-jedes-land/ (just click and you will learn the right precautions for your destination)
We cannot present you all parasites and diseases within our homepage. But we have compiled the most significant diseases in this section and in the travel diseases section.
Heartworm disease (dirofilariosis)
Heartworm disease is a disease that can occur in animals (mainly dogs, less frequently cats) and also in humans. The causative agent of dirofilariosis is Dirofilaria immitis, a type of nematode. The larvae of the heartworms are transmitted to the host by female mosquitoes (Culex). These migrate from the skin into the muscles, penetrate from there into the bloodstream and settle mainly in the right ventricle of the heart, the large pulmonary artery, the vena cava and occasionally in other organs. Depending on the infestation, massive restriction of heart function, shortness of breath and chronic cough occur. After being bitten by a mosquito, clinical symptoms of dirofilariasis appear after a few months, especially due to mechanical obstruction of the heart and vessels near the heart. The adult heartworms can be 15 - 35 cm long!
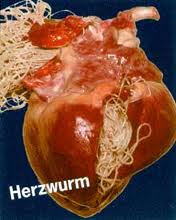
In the early stage, hardly any symptoms are noticeable in the dog. Later, coughing, loss of performance, weight loss, shortness of breath, congestion in the lungs, renal insufficiency and abdominal dropsy appear.
Inflammatory changes in the organs as well as dying parasites can cause thrombosis, which can be fatal. Cats are significantly less susceptible to dirofilariasis. The adult heartworms here have a lower viability and do not grow as large. However, many cats with heartworms show symptoms similar to dogs. Humans are actually a false host of the heartworm. Again, transmission occurs through mosquitoes and the worms settle in the pulmonary arteries. The symptoms of the disease are chest pain and cough, possibly with bloody sputum.
The occurrence of the disease is determined by the distribution of the specific mosquitoes. Meanwhile, the entire Mediterranean area is affected, but also the whole of France.
In Europe, dirofilariasis is common in:
- Italy: Po Valley and Tuscany
- France: especially Mediterranean area and Corsica
- Spain: southern provinces, Mallorca, Canary Islands
- Islands (Tenerife, La Palma)
- Portugal, Greece, Hungary and the Mediterranean
bordering Balkan countries - Switzerland: Individual cases are already known in Ticino!

Once the disease has been diagnosed (blood tests), it is treated with medication. However, life-threatening side effects may occur. In the case of a massive infestation, surgical removal of the worms from the heart must even be attempted.
Due to the great danger to patients posed by heartworms, prevention must be considered above all!
On the one hand, there is the possibility to expose dogs less to the risk of being bitten by such mosquitoes. If you absolutely want to have your darling with you during your vacations, you should keep in mind that there are particularly many mosquitoes around at dawn and dusk! Avoid wetlands and coastal regions. Use a parasite collar or spot-on preparation approved for heartworm-transmitting mosquitoes. And as the most important measure: heartworm prophylaxis deworming: A course just before departure, then at monthly intervals with a medication approved for this purpose. Consult your veterinary practice in time!

